When you connect a new USB device to your computer, Windows automatically detects the device and installs the appropriate driver. As a result, the user can use the connected USB drive or device almost immediately. If your organization’s security policy prohibits the use of portable USB storage devices (flash drives, USB hard drives, SD cards, etc.), you can block this behavior. In this article, we will show you how to block the use of external USB drives in Windows, prevent writing data to removable flash drives, or prevent executable files from running using Group Policy (GPO).
- Disabling USB Removable Drives in Windows with Group Policy
- Block USB Drives for Certain Users via GPO
- Disable Access to USB Drives via Registry and Group Policy Preferences
- How to Completely Disable USB Storage Devices in Windows?
- History of Connected USB Drives in Windows
- Allow Only Specific USB Storage Devices in Windows
Disabling USB Removable Drives in Windows with Group Policy
In Windows, you can flexibly manage access to external drives (USB, CD / DVD, etc.) using Active Directory Group Policies (we do not consider a radical way to disable USB ports through BIOS settings). You can block only USB drives, while other types of USB devices (mouse, keyboard, printer, USB to COM port adapters) that are not recognized as a removable disk will be available to the user.
We are going to block USB drives on all computers in a domain OU named Workstations. You can apply the USB restriction policy to the entire domain, but this will affect the servers and other technological devices.
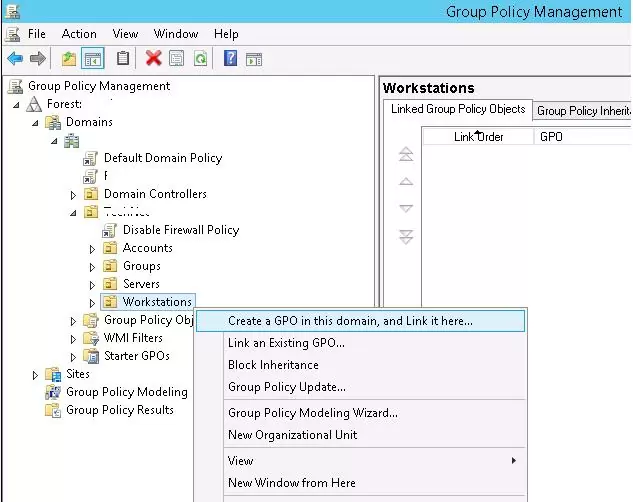
- Open the GPO management console (
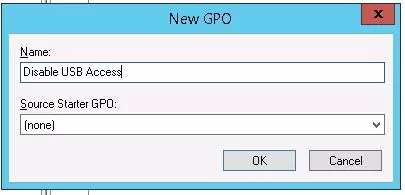
gpmc.msc), find the Workstations container in the Organizational Unit structure, right-click on it, and create a new policy (Create a GPO in this domain and Link it here);Tip. You can configure a policy to restrict the use of USB ports on a standalone computer (home computer or workgroup computer) using the Local Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc). - Set the GPO name “Disable USB Access”;
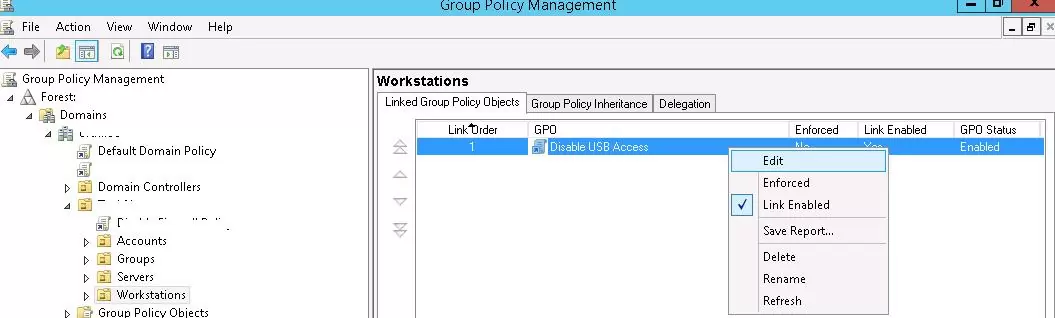
- Switch to GPO edit mode (Edit).
There are settings for blocking external storage devices in both the User and Computer Configuration sections of the GPO editor:
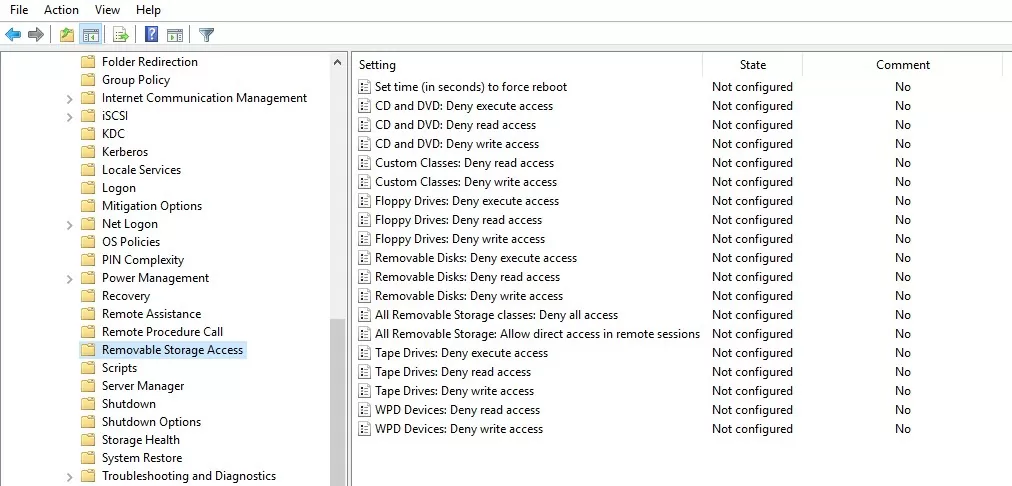
- User Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Removable Storage Access.
- Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Removable Storage Access.
In the Removable Storage Access section, there are several policies allowing you to disable the use of different types of storage classes: CD/DVDs, FDD, USB devices, tapes, etc.
- CD and DVD: Deny execute access.
- CD and DVD: Deny read access.
- CD and DVD: Deny write access.
- Custom Classes: Deny read access.
- Custom Classes: Deny write access.
- Floppy Drives: Deny execute access.
- Floppy Drives: Deny read access.
- Floppy Drives: Deny write access.
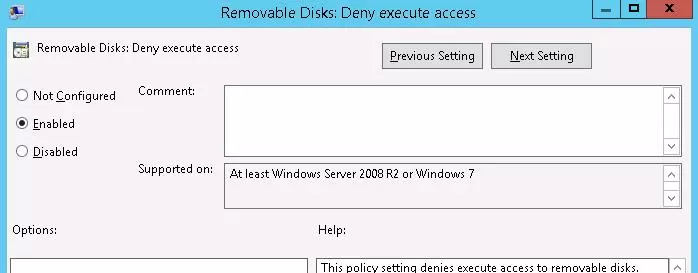
- Removable Disks: Deny execute access.
- Removable Disks: Deny read access.
- Removable Disks: Deny write access.
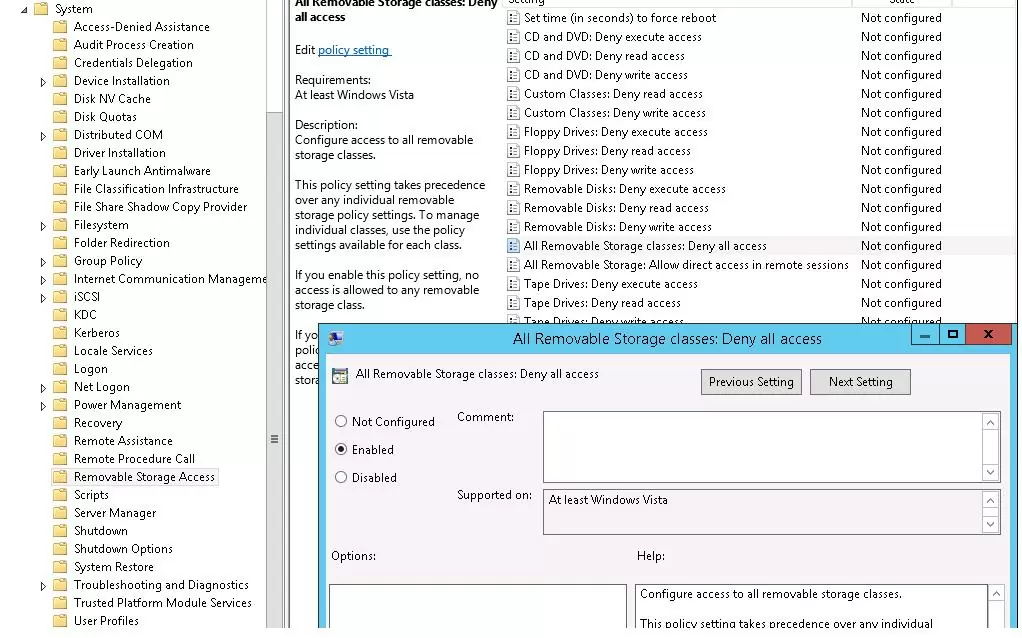
- All Removable Storage classes: Deny all access.
- All Removable Storage: Allow direct access in remote sessions.
- Tape Drives: Deny execute access.
- Tape Drives: Deny read access.
- Tape Drives: Deny write access.
- Windows Portable Device – this class includes smartphones, tablets, players, etc.
- WPD Devices: Deny write access.
As you can see, for each device class you can deny the launch of executable files (protect computers against viruses), prohibit reading data, and writing/editing files on external storage.
You can implement the “strongest” restrict policy All Removable Storage Classes: Deny All Access to completely disable the access to all types of external storage devices. To enable this policy, open its properties and change from Not Configured to Enabled.
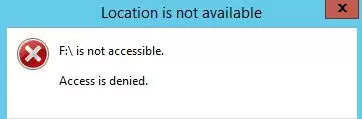
After enabling and updating the GPO settings on client computers (gpupdate /force), the Windows will detect the connected external devices (not only USB devices, but also any external drives), but when trying to open them, an error will appear:
Location is not available Drive is not accessible. Access is denied.
In the same policy section, you can configure more flexible restrictions on the use of external USB drives.
For example, to prevent writing data to USB flash drives and other types of USB removable storage, you should enable the policy Removable Disk: Deny write access.
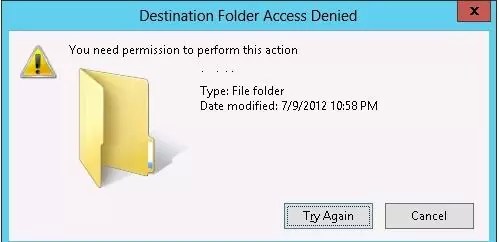
In this case, users will be able to read the data from the USB flash drive, but when they attempt to write information to it, they will receive an access denied error:
Destination Folder Access Denied You need permission to perform this action
You can prevent executable and script files from running from USB drives using the Removable Disks: Deny execute access policy.
Block USB Drives for Certain Users via GPO
Quite often it is necessary to block USB drives for all users in the domain except for administrators.
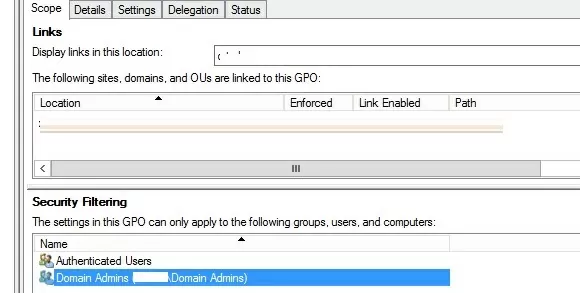
You can use the GPO Security Filtering to make an exception in a policy. For example, you want to prevent the USB blocking policy from being applied to the Domain Admins group
- Select your Disable USB Access policy in the Group Policy Management console;
- Add the Domain Admins group in the Security Filtering section;
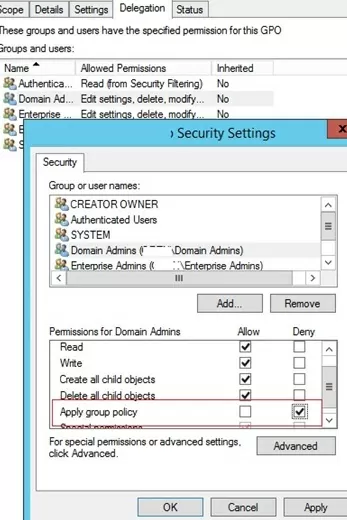
- Go to the Delegation tab and click the Advanced. In the security settings editor, specify that the Domain Admins group is not allowed to apply this GPO (Apply group policy – Deny).
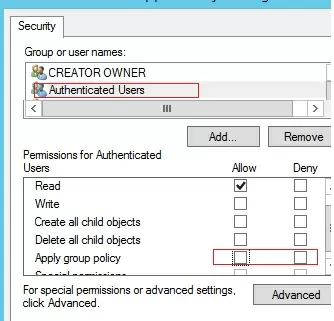
There may be another task – you need to allow the use of external USB drives to everyone, except for a certain group of users. Create a security group “Deny USB” and add this group to the security settings of the GPO. For this group, set permissions to read and apply the GPO, and leave only read permission for the Authenticated Users or Domain Computers group (by unchecking the Apply group policy checkbox).
Add users to this AD group who need to block access to flash drives and removable USB disks.
Disable Access to USB Drives via Registry and Group Policy Preferences
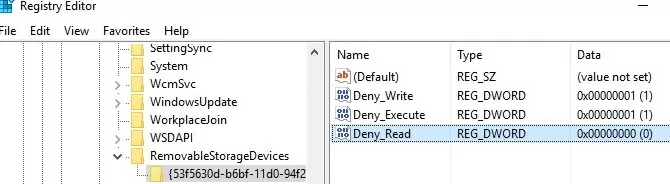
You can more flexibly control access to external devices by configuring the registry settings that are set by the policies discussed above via the Group Policy Preferences (GPP). All the above policies correspond to certain registry keys in the HKLM (or HKCU) \SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\RemovableStorageDevices key (by default this registry key is missing).
- To enable one of these policies, you must create a new subkey in the specified key with the GUID of the device class you want to block access to (column 2);
- In the new registry key, you need to create a REG_DWORD parameter with the name of the restriction that you want to implement:
Deny_Read — disable reading data from the media class;
Deny_Write – disable data writing;
Deny_Execute — denies running executable files from an external media class. - Set the parameter value:
1 — block the specified type of access to devices of this class;
0 – allow to use this class of devices.
| Group Policy Option | Device Class GUID | Registry parameter name |
| Floppy Drives: Deny read access | {53f56311-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Read |
| Floppy Drives: Deny write access | {53f56311-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Write |
| CD and DVD: Deny read access | {53f56308-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Read |
| CD and DVD: Deny write access | {53f56308-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Write |
| Removable Disks: Deny read access | {53f5630d-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Read |
| Removable Disks: Deny write access | {53f5630d-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Write |
| Tape Drives: Deny read access | {53f5630b-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Read |
| Tape Drives: Deny write access | {53f5630b-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b} | Deny_Write |
| WPD Devices: Deny read access | {6AC27878-A6FA-4155-BA85-F98F491D4F33} {F33FDC04-D1AC-4E8E-9A30-19BBD4B108AE} | Deny_Read |
| WPD Devices: Deny write access | {6AC27878-A6FA-4155-BA85-F98F491D4F33} {F33FDC04-D1AC-4E8E-9A30-19BBD4B108AE} | Deny_Write |
You can create the specified registry keys and parameters manually. In the screenshot below, I’ve created a RemovableStorageDevices key, and a subkey named {53f5630d-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b}. Using the REG_DWORD parameters, I prevented writing and running executable files from USB drives.
To quickly block reading and writing data to USB drives in Windows, you can run the following PowerShell script:
$regkey='HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\RemovableStorageDevices\{53f5630d-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b}'
$exists = Test-Path $regkey
if (!$exists) {
New-Item -Path 'HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\RemovableStorageDevices' -Name '{53f5630d-b6bf-11d0-94f2-00a0c91efb8b}' -Force | Out-Null
}
New-ItemProperty -Path $regkey -Name 'Deny_Read -Value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
New-ItemProperty -Path $regkey -Name 'Deny_Write' -Value 1 -PropertyType 'DWord' -Force | Out-Null
In a domain environment, you can deploy these registry parameters to user computers using Group Policy Preferences.
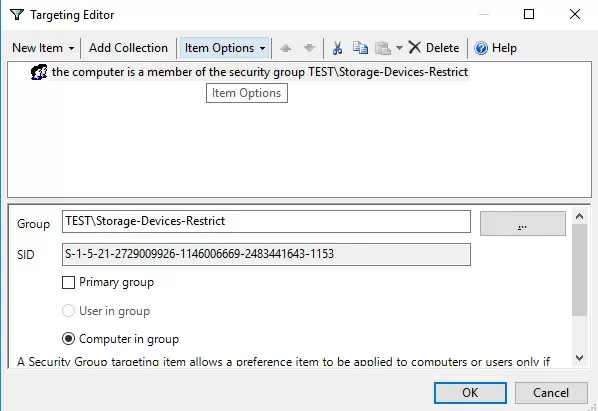
You can use these registry keys and GPP’s Item-level targeting to flexibly apply settings that restrict the use of external USB storage devices. You can apply policies to specific AD security groups, sites, OS versions, OUs (you can use even WMI filters).
For example, you can create the Storage-Devices-Restrict domain group and add the computer accounts for which you want to restrict the use of USB drives. This group must be specified in your GPP policy in the Item Level Targeting -> Security Group section with the Computer in Group option. This will apply the USB blocking policy to computers that are added to this AD group.
How to Completely Disable USB Storage Devices in Windows?
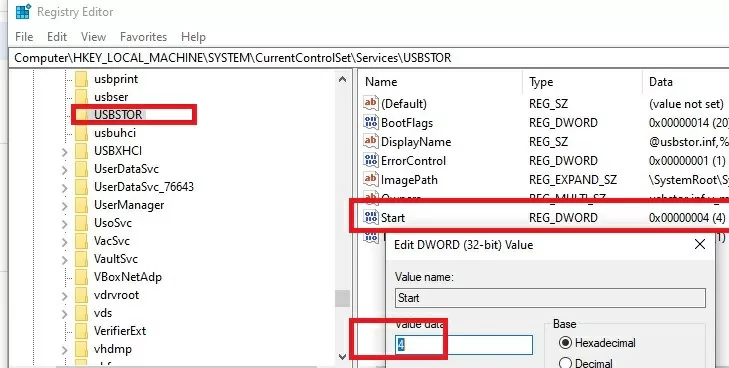
You can completely disable the USBSTOR (USB Mass Storage) driver, which is required to properly detect and mount USB storage devices.
On a standalone computer, you can disable this driver by changing the value of the Start registry parameter from 3 to 4. You can do this through PowerShell:
Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\USBSTOR" -name Start -Value 4
Restart your computer and try to connect your USB storage device. Now it shouldn’t appear in File Explorer or Disk Management console, and you will see a device driver installation error in Device Manager.
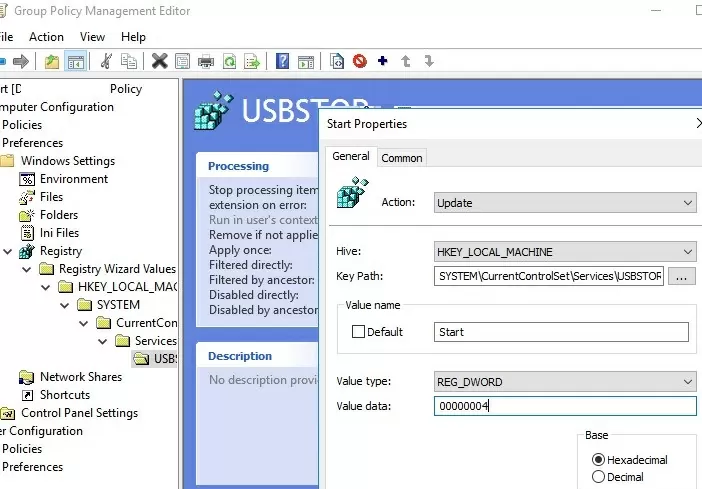
You can disable the USBSTOR driver from running on domain computers using Group Policy Preferences. To do this, you need to make changes to the registry through the GPO.
These settings can be deployed to all domain computers. Create a new Group Policy, link it to the OU with computers and in the Computer Configuration -> Preferences -> Windows Settings -> Registry section, create a new parameter with the values:
- Action: Update
- Hive: HKEY_LOCAK_MACHINE
- Key path: SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\USBSTOR
- Value name: Start
- Value type: REG_DWORD
- Value data: 00000004
History of Connected USB Drives in Windows
When troubleshooting USB media blocking policies, you need to get the information about the history of connecting USB drives to a computer.
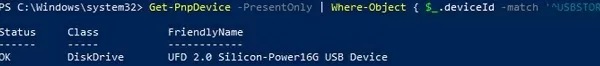
To list the USB drives currently connected to the computer, use the following PowerShell command:
Get-PnpDevice -PresentOnly | Where-Object { $_.deviceId -match '^USBSTOR' }
Status OK indicates that this USB drive is connected and working properly.
The Windows event log allows you to track events of connecting/ejecting USB drives.
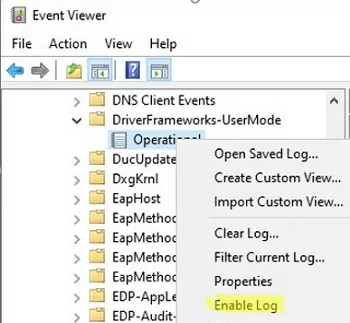
- You can find these events in Event Viewer -> Application and Services Logs -> Windows -> Microsoft-Windows-DriverFrameworks-UserMode -> Operational;
- By default, Windows doesn’t save a history of USB storage connections. So you will have to enable it manually (Enable Log) or via GPO;
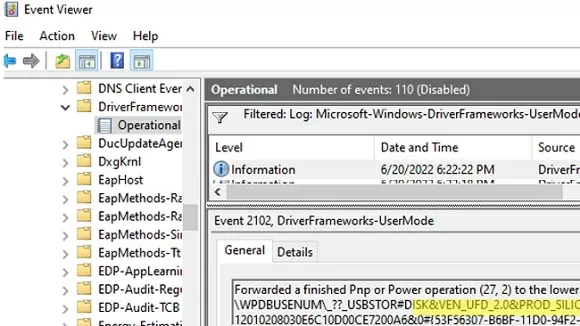
- Now you can use the EventID 2003 (
Pnp or Power Management operation to a particular device) to get information about when the USB drive was connected and Event ID 2102 (Pnp or Power Management operation to a particular device) about the ejection of the flash drive:Forwarded a finished Pnp or Power operation (27, 2) to the lower driver for device SWD\WPDBUSENUM\_??_USBSTOR#DISK&VEN_UFD_2.0&PROD_SILICON-POWER16G&REV_PMAP#89283229E6C10D23CE7200A2&2#{12234567-B6BF-11D0-2233-00A0AFBB3321F} with status 0x0.
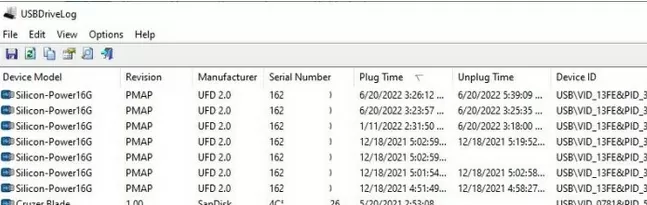
You can also use the free USBDriveLog tool from Nirsoft, which allows you to display the entire history of connecting USB drives to the user’s computer (displays information about the device, serial number, manufacturer, connection/disconnection time, and device id).
Allow Only Specific USB Storage Devices in Windows
On Windows, you can only allow certain (approved) USB drives to connect to your computer.
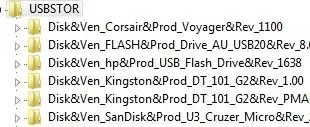
When you connect any USB storage device to the computer, the USBSTOR driver installs the device and creates a separate registry key under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USBSTOR. This registry key contains information about the USB drive (for example, Disk & Ven_Kingstom & Prod_DT_1010_G2 & Rev_12.00).
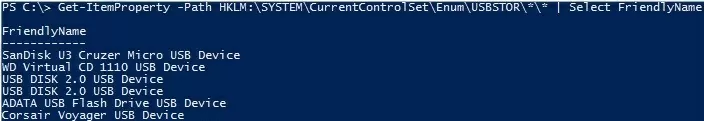
Get-ItemProperty –Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Enum\USBSTOR\*\*| select FriendlyName
Delete all entries for previously connected USB flash drives, except for the ones you need. Then you need to change the permissions on the USBSTOR registry key so that all users, including SYSTEM and administrators, have only read permissions. As a result, if you connect any USB drive other than the allowed one, Windows won’t be able to install the device.
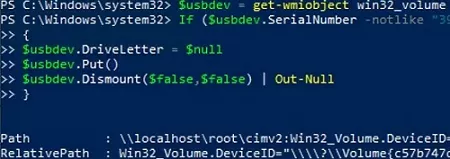
You can also run a specific command/script when a USB connecting EventID appears in the Event Viewer (here is a detailed example of how to run a process when a specific event occurs). For example, you can make a simple PowerShell script that automatically ejects any USB drives if the serial number doesn’t match the one given in the script:
$usbdev = get-wmiobject win32_volume | where{$_.DriveType -eq '2'}
If ($usbdev.SerialNumber –notlike “31DF1233BKAD”)
{
$usbdev.DriveLetter = $null
$usbdev.Put()
$usbdev.Dismount($false,$false) | Out-Null
Thus, you can perform the simplest check of USB flash drives connected to the computer.
20 comments
Have you test it on Windows 10?
I have tested it on Windows 10 Pro, but it is not work. The policy is applied but the USB is not denied.
AD is Windows Server 2008 r2 and Windows 10 admx is installed.
I have not tested this policy on clients Windovs 10.
Can you check that the policy is working correctly on older clients (Win 7, 8.1)?
I configured the GPO but it is not working on Win7. DC is 2008 R2.
The policy is applied but the USB is not denied.
Avez-vous pensé à désinstaller le périphérique USB au préalable ?
By mistake i made the same but i evoked the policy but the USB is still blocked im also using win server 2008R2
Can you teach how to limit to which user log-in to disable USB mass storage drive?
You can use GPO Security Filtering or GPO Delegation to allow/deny some users or group to apply this policy
A domain administrator disable usb access in GPO. How can i Enable in a local computer
Do you have local admin permissions on your workstation?
Hi, I applied this policy to the entire domain and added the administrators group as a deny as instructed above. When I go to test the usb as an administrator I can not access the usb.
What am I doing wrong?
Do you linked the “Disable USB Access” policy to an OU with computers or users? Which GPP section is configured?
We’re using ThreatLocker in our company. It’s easy to manage and allows creating organization, groups and computer policies for blocking USB devices, DVD/BD, etc. It also helps with permitting or denying path access to our fileservers and application whitelisting.
how to configure deny virtua usb
Hello
i followed your steps above and it worked perfectly
however, lets say i have a user named John Smith and want to grant access only to John smith and all other are blocked
how do i proceed??
Hi!…
.
Does “Network Discovery”… whether On or Off!… apply to Folders and/ or Files within one’s USB/ Flash Drive, or just Folders and/ or Files within one’s Hard Drive? And if the answer be the latter, then how can Folders and/ or Files within one’s USB/ Flash Drive be shielded from EXTERNAL NETWORK DISCOVERY (i.e., EXTERNAL to one’s LOCALLY NETWORKED computer/ computers) when one is interprocessing data between one’s USB/ Flash Drive and one’s Hard Drive, or between another LOCALLY CONNECTED USB/ Flash Drive, or other USBs/ Flash Drives connected to one’s LOCALLY NETWORKED computer/ computers?… and, whether– and for example– adding or removing Folders and/ or Files, or copying and/ or pasting Folders and/ or Files to and/ or from one’s Hard Drive(s), or to and/ or from another LOCALLY CONNECTED USB/ Flash Drive or other USBs/ Flash Drives.
.
Further, unless one has downloaded material from a “Web source” to one’s USB… the which, may result in one receiving a “hidden algorithm (e.g., a cookie)” that will “Discover” other personal content on one’s USB/ Flash Drive (like a “trojan algorithm” that/ which can “open one’s USB door” afterupon its entry into one’s system)… I can see no way that a web source should be able to “Discover” other content within one’s USB(s)/ Flash Drive(s) when one is “PASSIVELY USING” one’s USB/ Flash Drive in association with one’s Hard Drive (i.e., adding or removing NEUTRAL Folders and/ or Files, or copying and/ or pasting NEUTRAL Folders and/ or Files!… i.e., those “NONPROPRIETARILY TAGGED”, from PROPRIETARY DOWNLOADS). Nevertheless, if “Network Discovery” does not generally apply to USBs/ Flash Drives, then even PASSIVE FOLDERS AND FILES within one’s USB(s)/ Flash Drive(s) may be routinely Discovered hundreds, or even thousands of miles away (and within seconds) by any number of Web sources. And, unbeknown to hapless netizens.
.
In my case, I want to deny EXTERNAL NETWORK DISCOVERY by way of an EXTERNAL WEB SOURCE’s USB(s)/ Flash Drive(s), of any data/ content within my USB(s)/ Flash Drive(s) LOCALLY CONNECTED to my locally networked computer/ computers, and any data/ content within another LOCALLY CONNECTED USB/ Flash Drive, or other USBs/ Flash Drives… in contrast to denying a permitted LOCALLY CONNECTED USB/ Flash Drive or other USBs/ Flash Drives locally networked to my computer/ computers, set up to accesss data/ content within my locally networked computer’s/ computers’ Hard Drive(s), or within a locally networked USB/ Flash Drive or USBs/ Flash Drives. In other words, I want an allowed LOCALLY CONNECTED USB/ Flash Drive that/ which is connected to my locally networked computer/ computers to locally process data/ content (whether on a HDD/ HDDs, or on another LOCALLY CONNECTED USB/ Flash Drive or other USBs/ Flash Drives), but not an EXTERNAL WEB SOURCE’s USBs/ Flash Drives that/ which are not a part of my LOCALLY NETWORKED computer/ computers!
.
No emails please!
An alternative to all this is USB-Lock-RP.
Restore Missing CD/DVD Drive in Window by resetting the custom CD/DVD settings in the registry:
1) Start regedit.exe
2) Go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\{4D36E965-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}
3) Find and delete the keys UpperFilters and LowerFilters
4) Restart computer
Hello, I have followed the instructions in this tutorial, and my USB drive is now disabled, thank you! Now however, management would like several users to have USB access no matter what PC they log into. My ‘Block USB’ is a user policy, and now has an AD group with ‘deny apply GPO’, and the group of users still gets access denied to USB drives. It seems the policy cannot be ‘undone’ without unlinking the policy from the OU. Any ideas?
What exactly is the policy you are implementing to disable USB devices?
You should apply the settings using the User Configuration section rather than the Computer Configuration section. You can then use Security Filtering to make an exception to the policy.
It’s a better idea to assign a specific device to a user
and then to authorize:
specific devices, on specific machines
or
specific devices, on groups of machines.